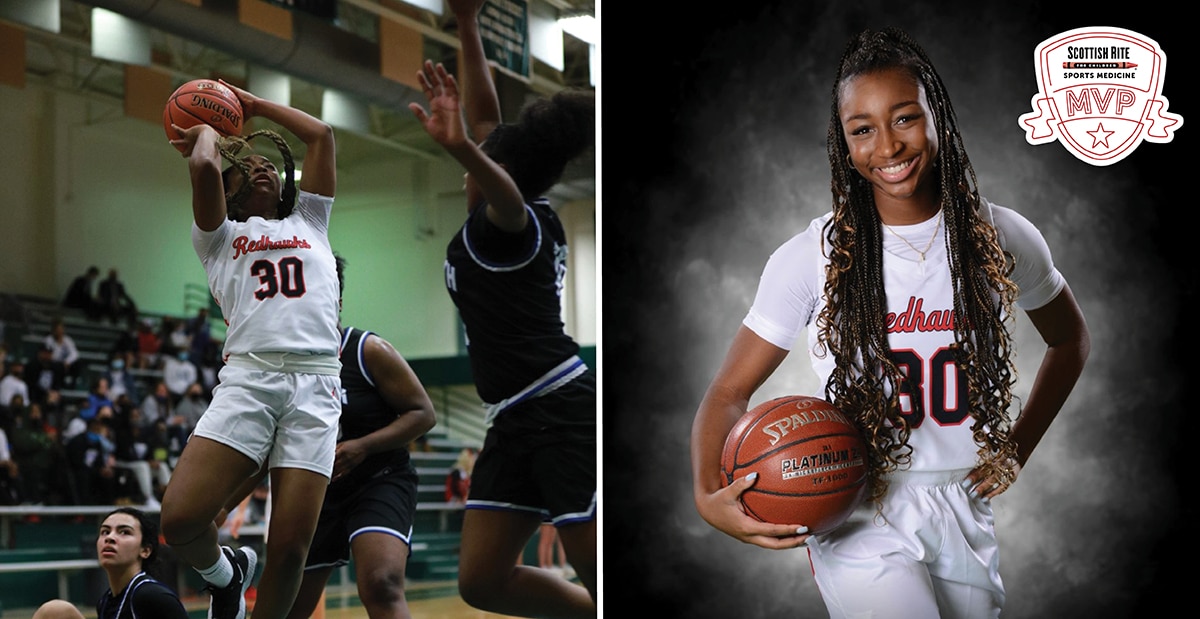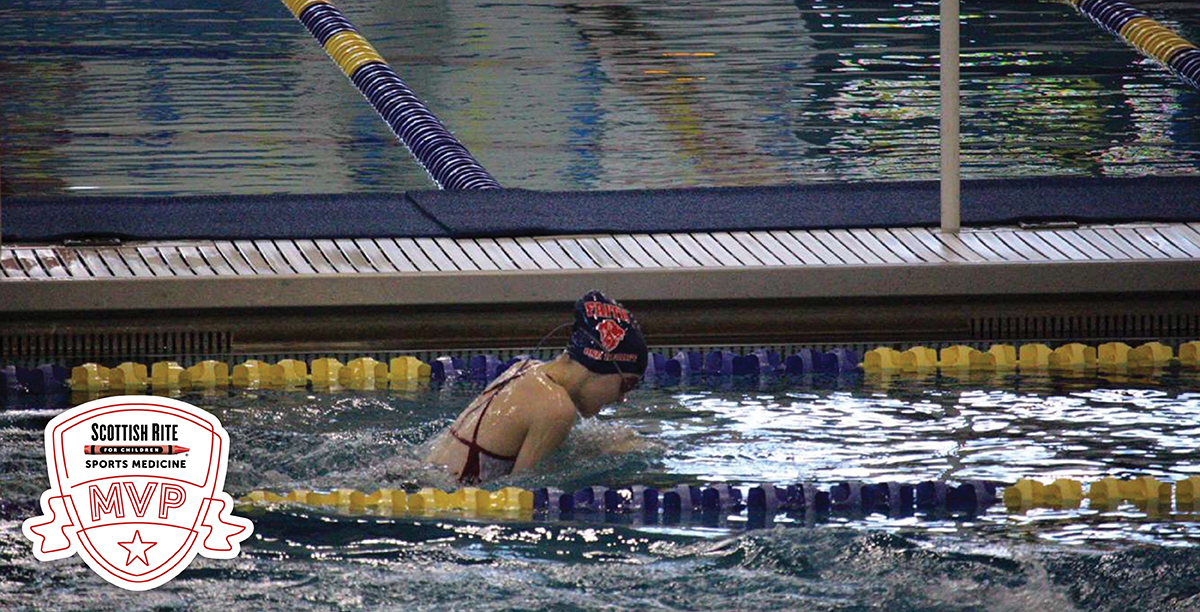Pediatric orthopedic surgeons Henry B. Ellis, M.D., and Philip L. Wilson, M.D., along with colleagues from the multicenter study group Factors Associated with Clavicle Treatment Study (FACTS) have published another set of findings in the American Journal of Sports...