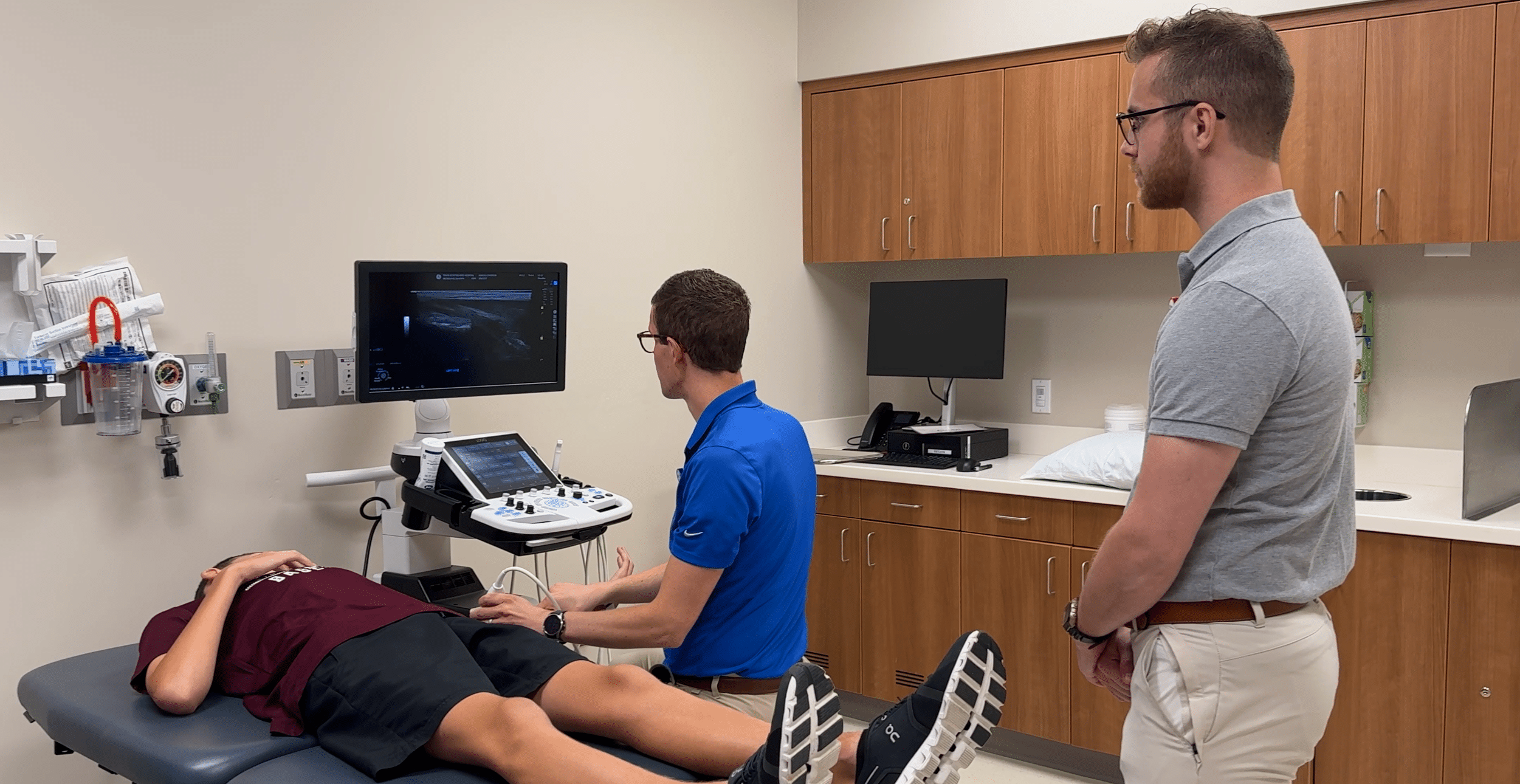
Ethan, of Richardson, Texas, has a deep passion for sports, especially baseball. As a dedicated catcher, the 11-year-old transforms into the reputable “Monster,” a nickname he earned for his fearless and determined presence behind the plate. “The nickname ‘Monster’...