Scottish Rite For Children Neurologist Steven Sparagana Honored With Legacy Fund
SCOTTISH RITE FOR CHILDREN NEUROLOGIST STEVEN SPARAGANA HONORED WITH LEGACY FUND
Fund will support tuberous sclerosis complex research
May 17, 2024 – The TSC Alliance® announced it has established the Steven Sparagana Legacy Fund to honor the upcoming retirement of Steven Sparagana, M.D., who served as Tuberous Sclerosis Complex (TSC) Clinic Director at Scottish Rite for Children in Dallas for 24 years and as a professor in the department of neurology at UT Southwestern Medical Center.
Tuberous sclerosis complex is a rare genetic disease that affects people at all stages of life. TSC causes tumors to grow in different organs and can impair their function, primarily the brain, heart, kidneys, skin, eyes and lungs. Nearly one million people worldwide are estimated to be living with TSC, with approximately 50,000 in the United States. Although there is no cure, there is hope. Research has proven that early diagnosis and intervention(s) are key for optimizing long-term outcomes. Advancements in research continue to deliver new and improved therapeutic options.
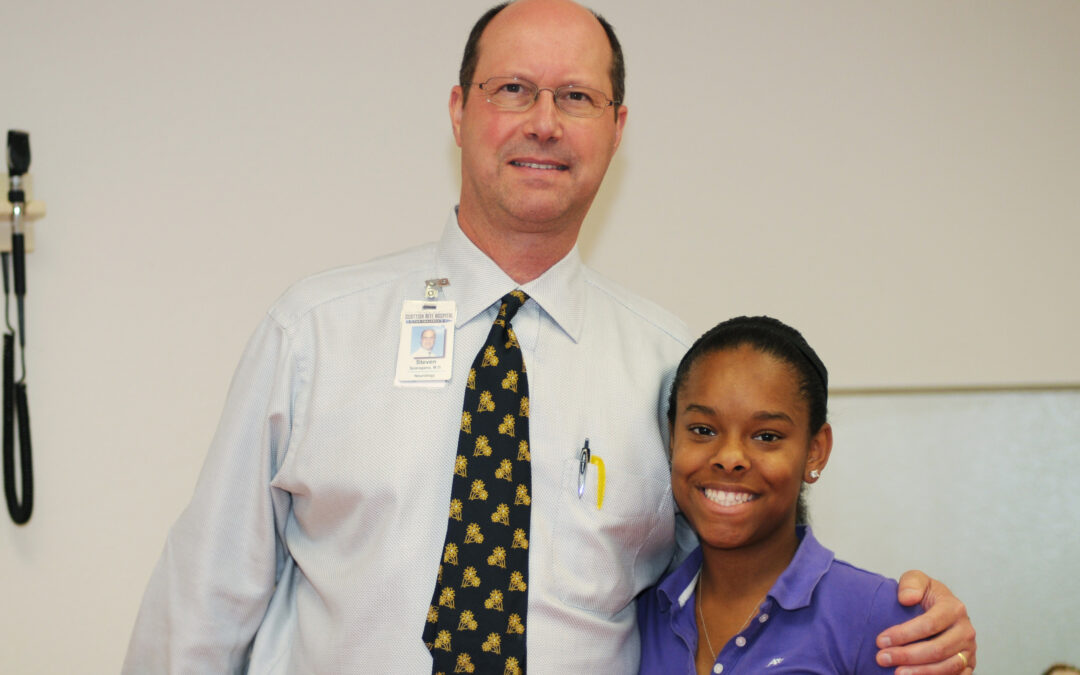
Steven Sparagana, M.D., with patients Gabby and Izzy, age 7, at an appointment for their ongoing treatment of tuberous sclerosis complex.
“The TSC Alliance is thrilled to create this fund to recognize Dr. Sparagana’s multiple contributions to TSC clinical care and research,” said Kari Luther Rosbeck, TSC Alliance President & CEO. “He also served on our organization’s Professional Advisory Board, and his early research helped create the TSC Natural History Database, which captures patient data to document the impact of the disease on a person’s health over his or her lifetime. The database now houses information on more than 2,600 people with TSC. His impact on the TSC community has been tremendous.”
In 2004, Dr. Sparagana’s original $141,307 grant from the TSC Research Program at the U.S. Department of Defense was the genesis of the TSC Natural History Database. He has since served as a member of the TSC Alliance’s Natural History Database/Biosample Repository Steering Committee, and Scottish Rite for Children was one of the original pilot sites for the database. His impact, particularly as it pertains to the Natural History Database and pivotal clinical trials, has been instrumental in improving the quality of life for individuals with TSC.
“Dr. Sparagana’s forward-thinking vision coupled with his kind and collaborative style enabled him to be a contributor and leader of multiple clinical research projects,” said Steven L. Roberds, PhD, TSC Alliance Chief Scientific Officer. “Additionally, in 2012, he chaired the development of a new section of TSC clinical consensus guidelines focused on the importance of integration of care to treat the ‘whole person’ living with TSC.”
The Steven Sparagana Legacy Fund will provide an ongoing source of revenue in support of the Natural History Database and Biosample Repository as a tribute to his contributions to the creation and ongoing success of these invaluable tools. Supporters can easily contribute online.
“I am grateful to the TSC Alliance for this honor. It has been a privilege to serve children, families and the community affected by tuberous sclerosis complex,” said Dr. Sparagana. “The Natural History Database and Biosample Repository have provided substantial contributions to TSC basic science and clinical research, and I wholeheartedly support these important endeavors. I am also thankful to Scottish Rite for Children, which has generously supported the hospital’s TSC Clinic for more than 30 years.”