Mar 29, 2018 / Hip Disorders
#SRHaccess Facebook LIVE Recap: Femoroacetabular Impingement
On this week’s Facebook live, Chief of Staff Daniel J. Sucato, M.D., M.S. joined us to discuss femoroacetabular impingement, also known as FAI. Below is a recap of the conversation.
Watch the segment.
What is femoroacetabular impingement (FAI)?
As young as nine years old all the way into early adulthood.
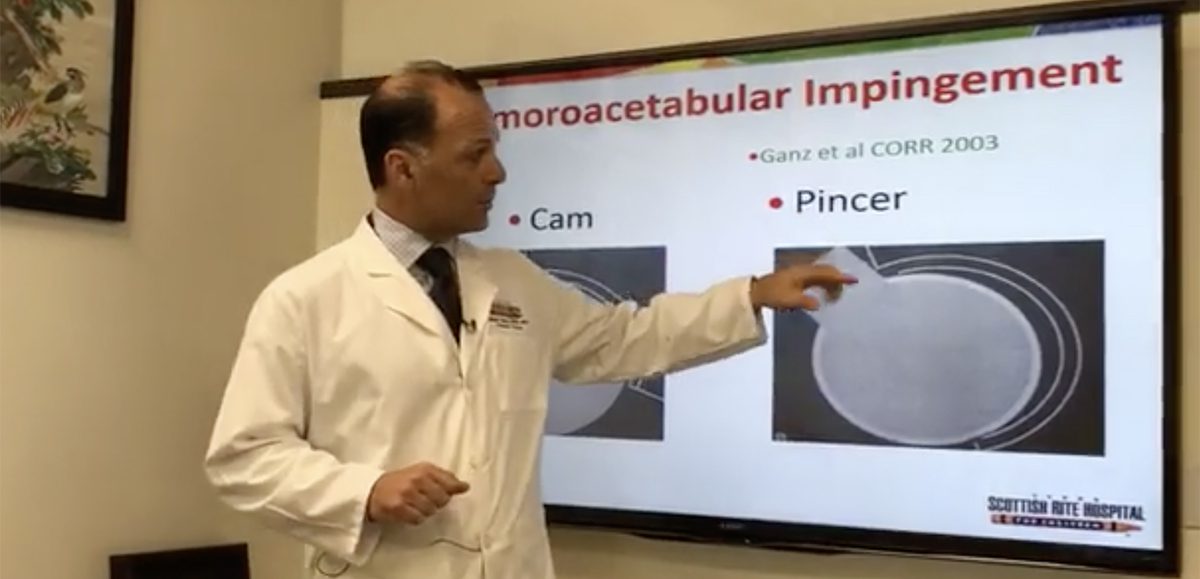
Two types of FAI:
Watch the segment.
What is femoroacetabular impingement (FAI)?
- The femur bone normally has a nice range of motion to internally and externally rotate.
- FAI occurs when the femur, as it flexes, impinges against the socket causing pain.
- Our specialists are seeing more and more patients who are active earlier on in life in a profound and consistent way.
- FAI normally occurs from an overuse injury during a certain activity or sport.
As young as nine years old all the way into early adulthood.
Two types of FAI:
- Cam impingement: primary problem is on the ball part of the hip. A little bump on the ball of the hip develops and when in flexion, hits up against the socket causing pain. The injury occurs to the socket cartilage at first.
- Pincer impingement: primary problem is on the socket side. There is too much overhang from the socket causing the pain. The injury occurs on the labrum at first.
- It is possible for an adolescent to have both types of FAI at once.
- Groin pain – pain at the front of the hip.
- Hip pain to the side is more muscle.
- At the beginning, pain is associated with FAI occurs during activities or sport.
- As it progresses, it could be painful to walk.
- Perthes disease – ball part of the hip takes on a bigger shape and could create a cam impingement.
- Slipped Capital Femoral Epiphysis (SCFE) – ball part of the hip slips out of place.
- FAI could be associated with a previous pediatric hip condition, however that is not always the case.
- Idiopathic FAI: otherwise healthy hip, but the condition develops over time with no cause.
- Depending on how active or position the patient plays, sports/activities where there is consistent hip flexion past 90 degrees.
- Figure skating, gymnastics, dancing, track
- Team approach to care: patients will be seen by several members of the health care team.
- Psychologists: understand the patient’s pain, understanding where the pain is generating from and if there are other factors causing the pain.
- Movement Science Lab: study the patient’s hip motion.
- Nursing staff, physical therapy and orthopedic doctor will see the patient.
- Advanced imaging – state-of-the art MRI.
- Physical therapy: stabilize the hip through strengthening and stretching.
- PT program specific to the patient’s needs and symptoms.
- Surgical treatment is determined depending on the patient and severity of their condition.
- Every adolescent hip patient gets enrolled in the Global Hip Study.
- The patient is asked specific patient related quality of life questions, which are answered on a tablet.
- Studies are conducted in the movement science lab to objectively measure range of motion, strength and gait.
- The purpose of this study is to demonstrate the differences in patients before and after treatment – what was successful versus what was not.



